The economy of sports is the most important part of the sphere of physical culture is professional sport, which represents the vertical, most advanced and
Professional sports economy

The most important component of the sphere of physical education is professional sport, which represents the vertical, most advanced and commercialized part of the entire aggregate of physical education and sports relations. Most amateur athletes would like to become professionals, big sport stars and actors of big business.
However, one desire is not enough to get into professional sport. Both novice and already prevailing athletes, non-professional athletes need to go through a maid of amateur sports, where the competition is very high. And only the most capable and purposeful people break through a sieve of hard selection in the sport elite – to the cohort of professionals (see Fig. 2.6).
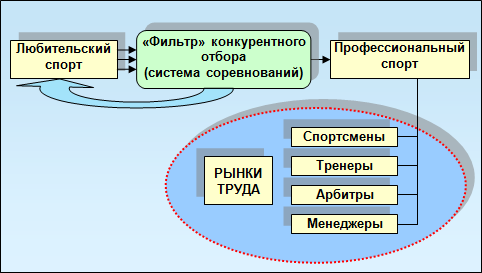
Fig. 2.6. The diagram of the relationship of amateur and professional sports.
Professional sport, like any elite group, is a small size of the bulk of athletes and physical education and does not usually exceed a mark of 0.1-0.5%. At the same time, in its cost and volume of cash flowing, it, as a rule, is repeatedly surpassed by amateur sport and is now a significant part of the world economy.
Professional sports services. As a branch of economic activity, professional sport produces a product for consumers in the form of spectacular services. Spectators receive psychological satisfaction from the consumption of sports and entertainment services and are therefore ready to pay them. Moreover, the higher the quality of the services provided (which is expressed in the prestige of the competition), the higher their price.
Spectacular services supplied by professional sports have their distinguishing features that make them unique in their properties. This uniqueness allows the spectacular mass services of professional sports to successfully compete with all other services of a similar properties and quality presented in show business markets.
The exclusivity of a professional sports product is the following specific features:
- In the elements constant novelty. Sports competitions are always a new sight that almost never repeats the previous one. Each new start, duel, game is a newly opened spectacle, an exciting and unforgettable event that attracts the attention of huge masses of people of various nationalities and religions;
- In elements Sustainability services. It is generally accepted that the service cannot be preserved, that is, the moment of its provision and consumption coincides in time. For many types of services, this statement is true (for example, for transport).Ekonomika_professionalnogo_sporta
- Professional sports economy The economy of sports is the most important part of the sphere of physical culture is professional sport, which represents the vertical, most advanced and, Professional sports economyThe most important component of the sphere of physical education is professional sport, which represents the vertical, most advanced and commercialized part of the entire aggregate of physical education and sports relations. Most amateur athletes would like to become professionals, big sport stars and actors of big business.
However, one desire is not enough to get into professional sport. Both novice and already prevailing athletes, non-professional athletes need to go through a maid of amateur sports, where the competition is very high. And only the most capable and purposeful people break through a sieve of hard selection in the sport elite – to the cohort of professionals (see Fig. 2.6).
Fig. 2.6. The diagram of the relationship of amateur and professional sports.
- Professional sport, like any elite group, is a small size of the bulk of athletes and physical education and does not usually exceed a mark of 0.1-0.5%. At the same time, in its cost and volume of cash flowing, it, as a rule, is repeatedly surpassed by amateur sport and is now a significant part of the world economy.
- Professional sports services
- . As a branch of economic activity, professional sport produces a product for consumers in the form of spectacular services. Spectators receive psychological satisfaction from the consumption of sports and entertainment services and are therefore ready to pay them. Moreover, the higher the quality of the services provided (which is expressed in the prestige of the competition), the higher their price.
Spectacular services supplied by professional sports have their distinguishing features that make them unique in their properties. This uniqueness allows the spectacular mass services of professional sports to successfully compete with all other services of a similar properties and quality presented in show business markets.The exclusivity of a professional sports product is the following specific features:
In the elements constant
- novelty. Sports competitions are always a new sight that almost never repeats the previous one. Each new start, duel, game is a newly opened spectacle, an exciting and unforgettable event that attracts the attention of huge masses of people of various nationalities and religions;
- In elements Sustainability
- services. It is generally accepted that the service cannot be preserved, that is, the moment of its provision and consumption coincides in time. For many types of services, this statement is true (for example, for transport).However, entertainment-mass services of professional sports have their own specifics. In particular, they have the property of persistence and reproducibility, that is, the same sports spectacle can be recorded on video and subsequently played back on television, via the Internet or on mobile phones. And every time the owner of the rights to a sports and entertainment service derives commercial benefits;AT
- mass charactercollectivity
consumption. Competitions of professional athletes almost always (with the exception of special forms of punishment when matches are played without spectators) are held in the presence of many fans, attracting increased attention from electronic and print media. In addition, sports games and championships are actively discussed among sports fans, among friends and colleagues. In other words, mass consumption is organically inherent in sports and entertainment services, that is, consumption by many people at once. It is this feature of a professional sports product that is used in advertising to obtain secondary economic effects, which consist in expanding the popularity and attractiveness of the advertised goods and services, and, as a result, stimulating sales and consumption.
Due to its high internal competitiveness, which requires constant high results and loads, the time spent by athletes in the professional sports system is limited. The average age of athletes leaving professional sports varies significantly depending on the sports, but on average does not exceed 35-37 years. This circumstance is essential for the economics of professional sports, since when the age threshold is reached, the athlete reduces his speed and strength indicators, and with them the quality of the service provided by the athlete decreases. As the quality decreases, so does the price of the service. As a result, the athlete needs to either change his role (to switch to the work of a coach, referee or manager) or leave professional sports.

